"In this blog post, I'll explore Web APIs within the browser context, which are the APIs provided to front-end developers by web browsers. These APIs are sometimes referred to as BOM (Browser Object Model) APIs."
What is Web Apis?
Web APIs in the context of a web browser refer to a set of built-in JavaScript interfaces and functions provided by the browser itself. These APIs enable web developers to interact with and manipulate various elements of web content, such as the Document Object Model (DOM), make HTTP requests to external resources, store data locally, access device features (e.g., geolocation), and create dynamic visual and interactive experiences within web pages. Web APIs are fundamental tools that empower developers to enhance the functionality and interactivity of web applications while ensuring compatibility across different browsers.
Now let us see some of the popular web APIs that every front-end developer should know.
1. DOM API (Document Object Model):
The DOM API allows developers to access and manipulate the structure and content of web pages, turning them into dynamic and interactive applications.
Some Common Methods/Functions:
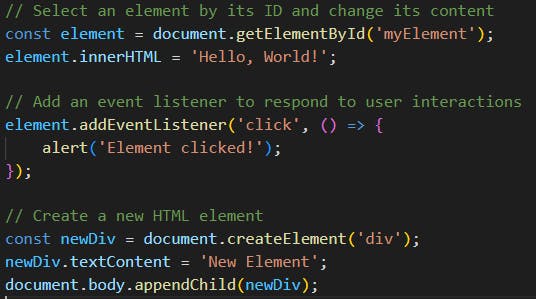
document.getElementById(id): Retrieves an element by its ID.element.innerHTML: Gets or sets the HTML content of an element.element.addEventListener(event, function): Attaches an event listener to respond to user interactions.document.createElement(tagName): Creates a new HTML element.
2. Fetch API:
The Fetch API simplifies making HTTP requests, fetching data from servers, and handling responses in a Promise-based manner.
Some Common Methods/Functions:
fetch(url, options): Initiates an HTTP request and returns a Promise.response.json(): Reads and parses a JSON response.response.text(): Reads and retrieves the response as text.response.status: Retrieves the HTTP status code.

3. localStorage and sessionStorage:
These Web Storage APIs provide a way to store data locally on the client-side, persistently with localStorage and for the duration of a session with sessionStorage.
Common Methods/Functions:
localStorage.setItem(key, value): Stores data in localStorage.localStorage.getItem(key): Retrieves data from localStorage.sessionStorage.setItem(key, value): Stores session-specific data.sessionStorage.getItem(key): Retrieves session-specific data.

4. Canvas API:
The Canvas API allows developers to create and manipulate graphics, draw images, and build animations directly in the browser.
This is a very powerful api a separate blog can be written for this api.
Common Methods/Functions:
getContext('2d'): Retrieves a 2D drawing context.context.fillStyle: Sets the fill color.context.fillRect(x, y, width, height): Draws a filled rectangle.context.drawImage(image, x, y): Draws an image on the canvas.

This is the output of the above code in the browser

5. WebSockets:
WebSockets enable real-time, bidirectional communication between the browser and a server, ideal for chat applications, online gaming, and live notifications.
Common Methods/Functions:
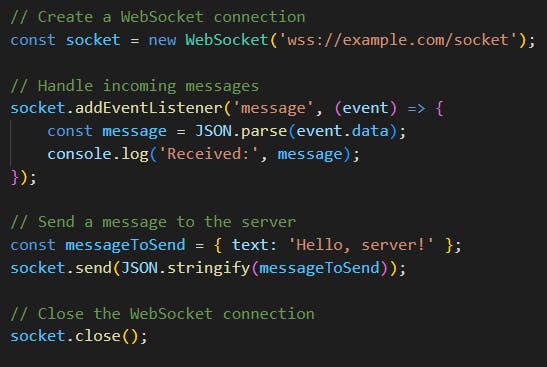
new WebSocket(url): Creates a new WebSocket connection.socket.send(data): Sends data to the server.socket.addEventListener('message', function): Handles incoming messages.socket.close(): Closes the WebSocket connection.
6. Console API:
The Console API allows developers to interact with the browser's console to log messages, errors, and debug information.
Common Methods/Functions:
console.log(message): Logs a message to the console.console.error(message): Logs an error message to the console.console.warn(message): Logs a warning message to the console.
Now let's look into some useful but lesser-known APIs
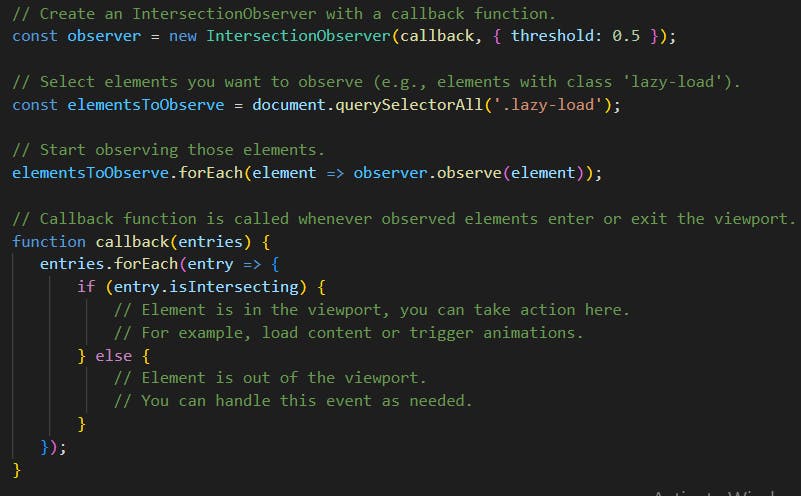
The Intersection Observer API is a powerful tool that allows you to efficiently track and respond to changes in the visibility of elements within a web page as they intersect with the viewport or another specified element. It is particularly useful for implementing various features like lazy loading images, infinite scrolling, or tracking when elements become visible in a user's viewport.
Common Methods/Functions: IntersectionObserver, observe(), isIntersecting
The MediaRecorder API allows web applications to record audio and video directly from the user's device camera and microphone. This API is useful for implementing features like audio/video recording, live streaming, and video conferencing within web applications.

We first access the user's media devices (camera and microphone) using
navigator.mediaDevices.getUserMedia().We create a
MediaRecorderobject to record from the media stream, specifying 'video/webm' as the MIME type for the recording.The
ondataavailableevent is set up to handle recorded data, which can be saved or processed as needed.Recording is started with
mediaRecorder.start().We set a timer to stop the recording after 10 seconds using
mediaRecorder.stop().Any errors encountered during the process are caught and logged to the console.
3.File and Directory Entries API (File System Access API):
The File and Directory Entries API, or File System Access API, provides web applications with secure and controlled access to the user's local file system. It enables the creation, reading, and writing of files and directories, making it a powerful tool for managing and manipulating local file data within a web application.

We request access to the file system using
showDirectoryPicker().If access is granted, we use the obtained
directoryHandleto create a file named 'example.txt' and write 'Hello, File System Access API!' into it.Proper error handling is implemented to deal with cases where access is denied or file operations fail.
The Web Speech API provides web applications with speech recognition and speech synthesis capabilities. It allows users to interact with web applications using voice commands and enables web applications to generate speech for various use cases, enhancing accessibility and interactivity.

We create a
SpeechRecognitioninstance to recognize speech input.The
onresultevent handler captures the recognized speech and logs it.We also create a
SpeechSynthesisinstance to generate speech with the provided text.The
speak()method is used to initiate speech synthesis.
There are more APIs like this you can explore mdn docs to know more about them.
